CCNP Enterprise 300-410 dumps exam questions Latest update! Contains 807 latest exam questions and answers! Covers complete CCNP Enterprise 300-410 ENARSI exam topics!
CCNP Enterprise 300-410 dumps are available in PDF and VCE formats, both formats contain the latest exam questions and answers. NOW! Download CCNP Enterprise 300-410 dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410. html
Use PDF and VCE to help you practice easily before the exam and pass the exam with a 100% guarantee of success.
Online practice part Latest CCNP Enterprise 300-410 dumps exam questions
| From | Number of exam questions | Associated certifications | Online Download |
| Pass4itsure | 13 | CCNP Enterprise | 300-410 PDF |
QUESTION 1:
Which control plane process allows the MPLS forwarding state to recover when a secondary RP takes over from a failed primary RP?
A. MP-BGP uses control plane services for label prefix bindings in the MPLS forwarding table
B. LSP uses NSF to recover from disruption *I control plane service
C. FEC uses a control plane service to distribute information between primary and secondary processors
D. LDP uses SSO to recover from disruption in the control plane service
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 2:
After an associate configured a DMVPN hub, you execute the following command on the hub router:
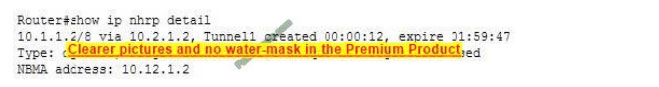
Which of the following statements is true of this output?
A. The NMBA address was statically configured
B. The NHRP information did not come from the NHS
C. The mapping was created through an NHRP registration request
D. The device at 10.1.1.2 is behind a NAT router
Correct Answer: C
The mapping was created through an NHRP registration request, as indicated by the flag setting registered. Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) can be used in place of static IP address to NBMA address mappings to allow the spoke routers in an mGRE hub-and-spoke configuration to discover one another\’s physical IP addresses.
When the output of the show nhrp detail command shows the registered flag listed, it means that the mapping was created dynamically and was learned through a registration request to the next hop server (NHS).
The mapping was not created statically. Had it been created statically, the Type field would not be listed as dynamic. It would say static.
The NHRP information DID come from the next hop server (NHS). That is indicated by the presence of the authoritative flag. The NHS is the next hop to the destination as indicated by the routing table.
The device at 10.1.1.2 is not necessarily behind a NAT router. The presence of the nat flag in the output indicates that the device at 10.1.1.2 supports the NHRP NAT extension type for supporting dynamic spoke-to-spoke tunnels to or from spokes behind a NAT router. This flag does not mean that the spoke (NHS client) is behind a NAT router.
Objective:
VPN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe DMVPN (single hub)
References:
Home > Support > Product support > Cisco IOS and NX-OS software > Cisco IOS software releases 12.4 mainline > Configure > Feature Guides > NHRP
QUESTION 3:
You are planning the configuration of Easy Virtual Networking (EVN).
Which of the following statements is true of an interface that will be an EVN trunk?
A. It must support 802.1q encapsulation
B. The interface can also be configured for VRF-Lite
C. The interface will support OSPFv3
D. The interface can support RIP
Correct Answer: A
The interface must be able to support 802.1q encapsulation. The EVN trunk carries the traffic of multiple virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instances, with the traffic of each instance tagged with an ID called the virtual network tag.
Since the VLAN ID field of an 802.1q encapsulated packet is used for this ID, the link must be one that supports 802.1q.
Easy Virtual networking is a technology that allows for the creation of separate networks with separate routing tables and routing instances using the same physical topology. The IP addressing for the networks can even overlap with no problem.
The networks are kept separate using the network ID tags in a similar fashion to the way switches keep VLANs separate by using VLAN tags.
An EVN trunk interface cannot also be configured for VRF-Lite. VRF-Lite is an earlier technology that accomplishes the same goal but lacks the simplicity of EVN.
Neither RIP nor OSPFv3 is supported in Easy Virtual Networking EVN at all.
Objective:
VPN Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe Easy Virtual Networking (EVN)
References:
Cisco > Easy Virtual Network Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S > Overview of Easy Virtual Network
QUESTION 4:
You instructed your associate to configure Router R2 to reject a redistribution of the 20.0.0.0/8 network, while still receiving routes from other networks connected to Router R1. The diagram below displays the network in place:
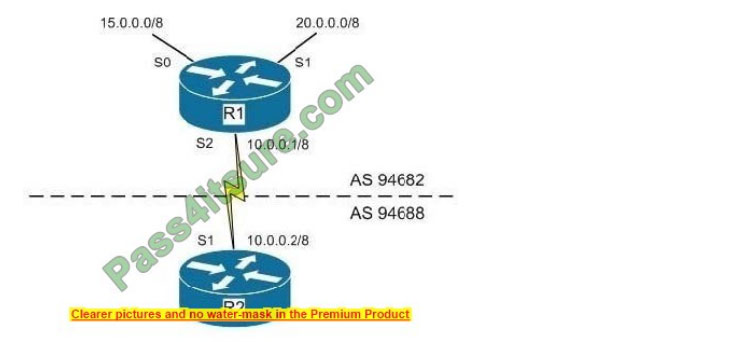
When he is finished, you find that the 20.0.0.0/8 network is still being advertised and traffic from the 20.0.0.0/8 network is not reaching Router2. You execute the show running-configuration command and see the following output:

What is the problem?
A. The access list was applied to the wrong interface.
B. The access list should have been configured as a distribution list.
C. The access list has an incorrect wildcard mask.
D. The access list is applied in the wrong direction.
Correct Answer: B
The access list should have been created as a distribution list to control route redistribution from the other area. This configuration would prevent the redistribution of the 20.0.0.0/8 network by applying the list as a distributed list under the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
The proper commands would be:
Router2(config)# router bgp 94688
Router2(config-router)# distribute-list 101 in
To correct the problem with traffic not arriving from the 20.0.0.0/8 network, you must remove the application of the list under interface S0 as well. This would be done by executing the following command set:
Router2(config)# interface Serial1
Router2(config-int)# no ip access-group 101 in
The access list was not applied to the wrong interface. It should not have been applied directly to any interface. When applied directly as an access list to an interface, it will prevent traffic, but not the redistribution of routes.
The access list does not have an incorrect wildcard mask. To prevent the redistribution of a Class C network, the correct wildcard mask is 0.0.0.255.
The access list was not applied in the wrong direction. It should be applied in the coming but should be applied as an incoming distribute-list, and it should be applied under the BGP protocol.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify filtering with any protocol
References:
Cisco IOS Master Command List, Release 12.4T > d > distribute-list in (IP) Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > Filtering Routing Updates on Distance Vector IP Routing Protocols
QUESTION 5:
You need to resolve a route-selection problem in a redistributed network by increasing the administrative distance to several networks for a protocol, other than EIGRP or BGP so that these routes will not be used. You create an access list 5 to identify the relevant networks and access the routing protocol configuration prompt.
Which command will set the administrative distance to these networks to 220 for the selected protocol?
A. Router(config-router)# list 5 distance 220
B. Router(config-router)# admin 220 access-list 5
C. Router(config-router)# distance 220 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 5
D. Router(config-router)# increase 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 admin 220 list 5
Correct Answer: C
The correct command is Router(config-router)# distance 220 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 5. This command instructs the router to change the AD for any networks specified in the access list 5 to 220.
The correct syntax for the distance command is shown below:
distance weight [address mask [ access-list-number | name]
The weight parameter is the administrative distance (AD), which is a number from 10 to 255. Note: Distances 0 through 9 are reserved for system use.
To change the administrative distance for an entire routing protocol, use the distance command, as shown below:
Router(config)# router rip
Router(config-router)# distance 125
To change the AD for only selected networks, use an access list with the distance command as shown below:
Router(config)#access-list 5 permit 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
Router(config)#access-list 5 permit 11.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
Router(config)#access-list 5 permit 12.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)# distance 220 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 5
The 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 portion included with the distance command could hold an address/mask combination for a single address, but it is more common to use an access list.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe administrative distance
References:
Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: Protocol-Independent Command Reference > distance (IP)
QUESTION 6:
Refer to the exhibit
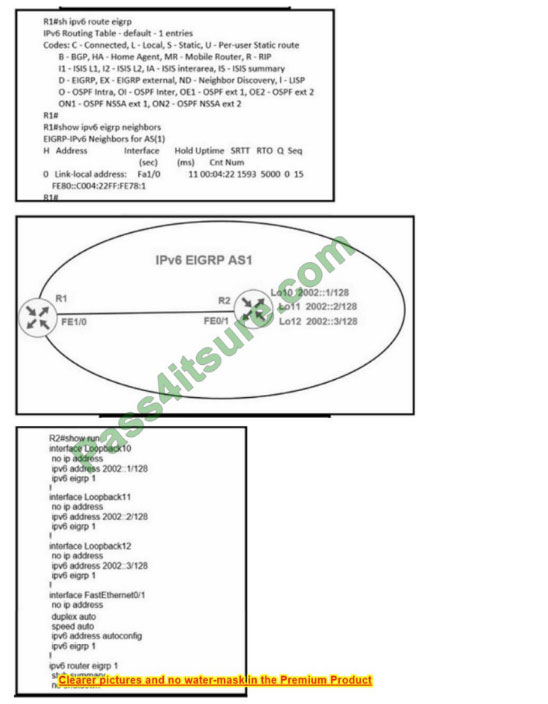
R1 cannot receive the R2 Interfaces with individual prefixes. What must be reconfigured to advertise R2 Interfaces to R1?
A. EIGRP process on R2 by removing the stub command Keyword summary
B. interface FastEthernet0/1 on R2 with an EIGRP summary for all three loopback prefixes
C. EIGRP process on R2 with the command stub summary receive-only
D. ElGRP process on R2 with the command stub summary connected
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 7:
Which statement about route distinguishers in an MPLS network is true?
A. Route distinguishers allow multiple instances of a routing table to coexist within the edge router.
B. Route distinguishers are used for label bindings.
C. Route distinguishers make a unique VPNv4 address across the MPLS network.
D. Route distinguishers define which prefixes are imported and exported on the edge router.
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 8:
What is the advantage of implementing BFD?
A. BFD provides faster updates for any flapping route.
B. BFD provides millisecond failure detection
C. BFD is deployed without the need to run any routing protocol
D. BFD provides better capabilities to maintain the routing table
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 9:
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator sets up an OSPF routing protocol for a DMVPN network on the hub router.
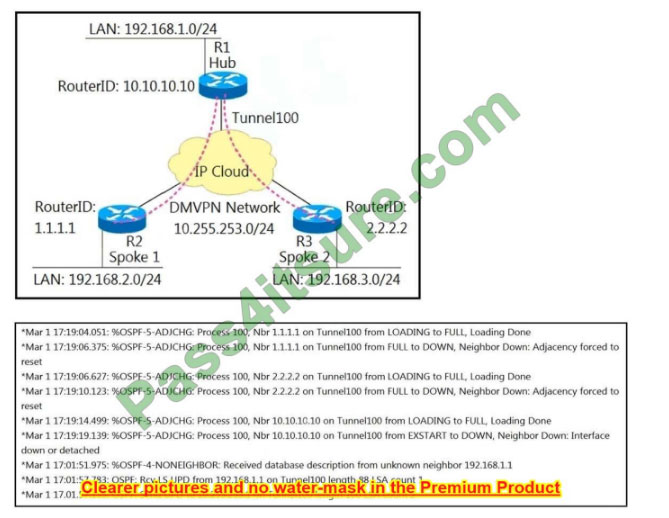
Which configuration command is required to establish a DMVPN tunnel with multiple spokes?
A. ip ospf network point-to-point on the hub router
B. ip ospf network point-to-multipoint on one spoke router
C. ip ospf network point-to-multipoint on both spoke routers
D. ip ospf network point-to-point on both spoke routers
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 10:
Refer to the exhibit.

An IT staff member comes into the office during normal office hours and cannot access devices through SSH Which action should be taken to resolve this issue?
A. Modify the access list to use the correct IP address.
B. Configure the correct time range.
C. Modify the access list to correct the subnet mask
D. Configure the access list in the outbound direction.
Correct Answer: A
To ACL should be permitted tcp 101 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
QUESTION 11:
Refer to the exhibit. The control plane is heavily impacted after the CoPP configuration is applied to the router. Which command removal lessens the impact on the control plane?
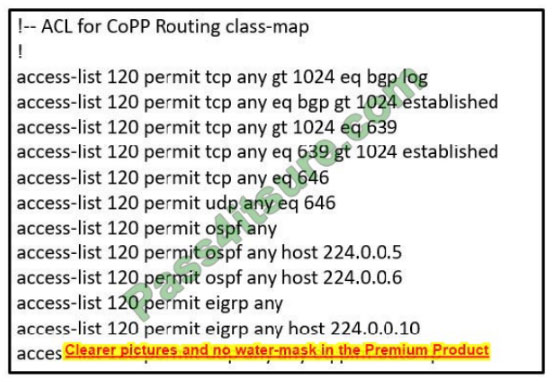
A. access-list 120 permit eigrp any host 224.0.0.10
B. access-list 120 permit ospf any
C. access-list 120 permit udp any eq pim-auto-rp
D. access-list 120 permit tcp any gt 1024 eq bgp log
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 12:
The following access lists are applied to an interface connecting two OSPF routers:
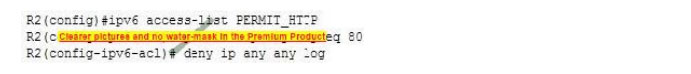
What is the result?
A. the DR on the link will begin updating
B. the OSPF adjacency will go down
C. the last deny statement will fail to log traffic
D. the list will only permit IPv6 neighbor advertisements
Correct Answer: B
If this list is applied to the interface connecting two OSPF routers, the OSPF adjacency would go down. They deny ip any log statement that will deny the IPv6 link-local addresses, which are used for the neighbor discovery process and by OSPF routers to establish neighbor adjacencies when directly connected.
By default, IPv6 access lists have a deny-all at the end that does NOT include those addresses. However, when you set an explicit deny as shown in the scenario, you will block all traffic that is not specified by an earlier statement in the list.
The DR on the link, if present, will not begin updating because the adjacency will fail. It will then have no neighbors to update.
The last deny statement in the scenario will log any traffic it blocks, as indicated by the inclusion of the log keyword.
The list will NOT permit neighbor advertisements. These are always done in terms of link-local addresses, which explicitly deny ip any log statement at the end will block.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security Sub-Objective: Configure and verify router security features References: Security Configuration
Guide: Access Control Lists, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S > IPv6 Access Control Lists Cisco > Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference > ipv6 access-list Cisco > Cisco IOS Security Command Commands M to R > permit
(IP) Cisco > Cisco IOS Security Command Commands D to L > deny (IP)
QUESTION 13:
Refer to the exhibit. Which action restores OSPF adjacency between R1 and R2?
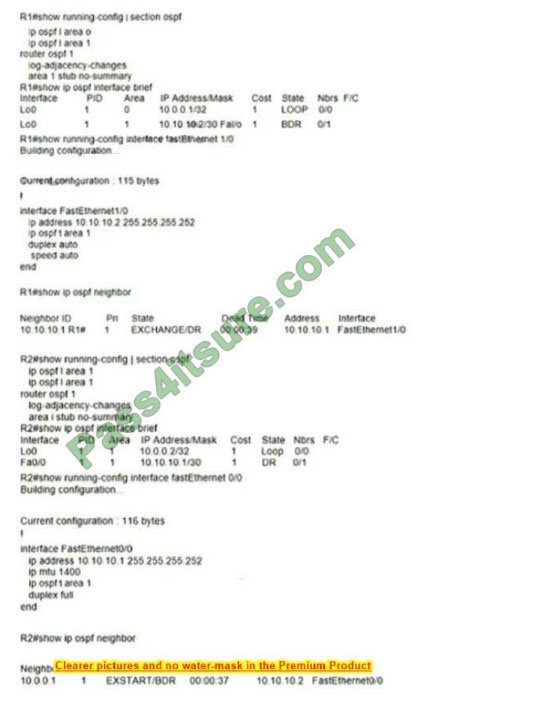
A. Change the IP MTU of R1 Fa1/0 to 1300
B. Change the IP MTU of R2 Fa0/0 to 1300
C. Change the IP MTU of R1 Fa1/0 to 1500
D. Change the IP MTU of R2 Fa0/0 to 1500
Correct Answer: D
…
CCNP Enterprise 300-410 exam “Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)” includes (Layer 3, VPN services, Infrastructure Security, Infrastructure services, and Infrastructure automation) topic exam.
Use the latest CCNP Enterprise 300-410 dumps covering the full subject exam: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html
Help you practice (PDF+VCE) easily and pass the exam with 100% success.



